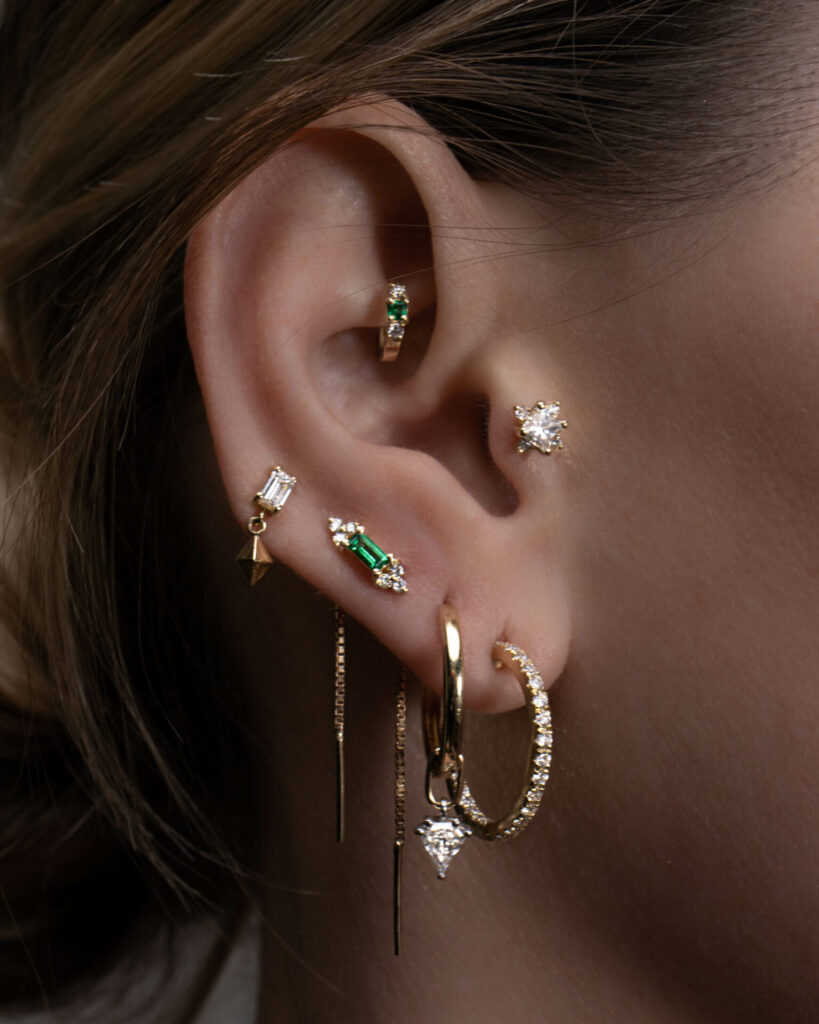
If you’ve ever considered getting your ears pierced or if you’re simply interested in learning about the art of ear piercing, then “The Art of Ear Piercing” is the perfect product for you. This comprehensive guide provides you with all the information you need to know about ear piercing, from the different types of piercings to the aftercare process. With step-by-step instructions and expert tips, you’ll become an ear piercing pro in no time. Whether you’re a newbie or a seasoned piercing enthusiast, “The Art of Ear Piercing” is your go-to resource for all things ear piercing.

This image is property of malkajewelry.com.
History of Ear Piercing
Ancient Cultures and Ear Piercing
Ear piercing has a long and rich history that dates back to ancient times. Some of the earliest evidence of ear piercing can be found in ancient Egyptian and Mesopotamian cultures, where it was a common practice among both men and women. In these societies, ear piercing held significant cultural and social significance, often symbolizing wealth, status, and even religious beliefs. It was also believed to have protective and therapeutic properties.
Ear Piercing in Different Time Periods
As time went on, ear piercing spread to different cultures and took on various forms. In ancient Rome, for example, ear piercing was primarily associated with slaves and later became popular among soldiers. During the Renaissance period, ear piercing was fashionable among nobles and the upper class in Europe. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, ear piercing gained popularity in Western societies, particularly among women, as a form of style and self-expression.
Evolution of Ear Piercing Techniques
The techniques used for ear piercing have evolved throughout history. In ancient times, simple tools like thorns, bones, and sharp stones were used to create ear piercings. Over time, the development of metalworking enabled the creation of more intricate and decorative jewelry, such as gold earrings adorned with gems. Today, modern ear piercing techniques involve the use of sterile needles or piercing guns, along with a wide variety of jewelry options to suit individual preferences.
Types of Ear Piercings
Standard Lobe Piercing
The standard lobe piercing is the most common type of ear piercing, usually placed on the lower fleshy part of the earlobe. It is a relatively quick and easy procedure, making it a popular choice for both children and adults. The jewelry worn in a standard lobe piercing can range from simple studs to more elaborate hoops and dangly earrings.
Helix and Cartilage Piercing
The helix and cartilage piercings are located on the upper part of the ear. The helix piercing is placed on the prominent outer rim, while the cartilage piercing can be done in various places along the inner and outer cartilage. These piercings are known for their versatility, allowing individuals to showcase a wide array of jewelry styles, including studs, hoops, and cuffs.
Tragus Piercing
The tragus piercing is positioned on the small piece of cartilage located just in front of the ear canal. This type of piercing can be quite stylish and eye-catching, as it highlights the unique anatomy of the ear. jewelry options for tragus piercings can include small studs or hoops that complement the shape of the tragus.
Daith Piercing
The daith piercing is situated on the innermost fold of cartilage, closer to the ear canal. It has gained popularity in recent years for its potential to alleviate migraines, although scientific evidence for this is limited. This piercing can be adorned with various jewelry styles, such as rings or curved barbells, which can add a touch of individuality to one’s look.
Rook Piercing
The rook piercing is placed on the upper part of the inner ridge of cartilage in the middle of the ear. It offers a unique and edgy look, making it a popular choice among individuals seeking a more unconventional ear piercing. Jewelry options for the rook piercing include curved barbells, captive bead rings, and curved barbells with decorative charms.
Conch Piercing
The conch piercing is positioned on the concave bowl-shaped area of cartilage in the middle of the ear. It can be divided into two types: inner conch piercing, done in the inner part of the bowl, and outer conch piercing, done in the outer part of the bowl. Both types offer ample space for a variety of jewelry styles, such as studs, hoops, and spirals.
Industrial Piercing
The industrial piercing, also known as a scaffold piercing or bar piercing, involves two holes connected by a long straight barbell or piece of jewelry. These holes are positioned diagonally across the upper part of the ear, usually passing through the helix and the antihelix. This piercing allows for the display of unique and striking jewelry pieces that span the entire length of the ear.
Snug Piercing
The snug piercing is situated on the inner ridge of cartilage above the antitragus. It is known for its snug and close-fitting appearance, which can enhance the overall aesthetics of the ear. Jewelry options for the snug piercing range from captive bead rings to curved barbells, providing individuals with plenty of possibilities to personalize their ear piercings.
Tash Rook Piercing
The tash rook piercing, also known as the faux rook piercing, is a creative alternative for those who want the look of a rook piercing without the need to pierce through the actual rook. It involves placing a barbell or curved jewelry piece through a fold of cartilage immediately above the tragus. This type of piercing offers a subtle yet distinctive addition to an ear piercing collection.
Outer Conch Piercing
The outer conch piercing is positioned on the outer cartilage area just before the curve where the conch meets the helix. It provides a unique placement for jewelry, showcasing a variety of styles, such as studs or hoops. This type of piercing allows for additional embellishments and creativity, giving individuals the opportunity to showcase their personal style.
Choosing an Ear Piercing Studio
Cleanliness and Sanitation Standards
When choosing an ear piercing studio, it is crucial to prioritize cleanliness and sanitation. Ensure that the studio follows strict protocols for sterilization, such as using single-use disposable needles or properly sterilizing piercing guns. The studio should have a clean and organized environment, with staff members who prioritize hygiene and take necessary precautions to prevent infections.
Experience and Qualifications of Piercer
Look for a studio with experienced and qualified piercers. The piercers should have proper training and certification in performing ear piercings. Ask about their experience and inquire about any specialized training they may have undergone. A skilled piercer can make the process smoother and minimize the risk of complications.
Rating and Reviews
Check the studio’s ratings and reviews to gauge the experiences of past clients. Look for positive feedback regarding their cleanliness, professionalism, and the overall quality of their services. Reviews can provide valuable insights into the studio’s reputation and the satisfaction of previous clients.
Availability of Jewelry Options
A good ear piercing studio should offer a wide selection of jewelry options to cater to individual preferences. From basic studs to intricate hoops and custom designs, having a variety of choices ensures that you find the perfect jewelry to suit your style and needs. The studio should also provide information on the materials used in their jewelry to ensure safety and minimize the risk of allergic reactions.
Consultation and Aftercare Services
An ideal ear piercing studio will offer consultations to address any concerns or questions you may have before getting pierced. They should provide thorough aftercare instructions and guidance, helping you take care of your new piercings properly. The studio should also be readily available to answer any post-piercing queries or provide assistance during the healing process.
Preparation for Ear Piercing
Selecting the Location
Before getting your ear pierced, consider the specific location where you want your piercing. Think about the type of piercing you desire and how it will complement your overall ear anatomy. Certain piercings may have limitations based on your ear’s structure, so consult with a professional piercer for guidance on the best placement options.
Choosing Jewelry
Selecting the right jewelry for your ear piercing is crucial, as it determines both the aesthetics and comfort of your piercing. Consider factors such as the material, style, and size of the jewelry. Opt for high-quality materials like surgical stainless steel, titanium, or 14k gold to minimize the risk of allergic reactions and ensure durability.
Evaluating Pain Tolerance
It’s essential to evaluate your pain tolerance before getting an ear piercing. Different individuals have varying pain thresholds, and while ear piercing is generally considered to be a low-pain procedure, some people may experience discomfort. If you have concerns about pain, talk to your piercer, who can provide information on pain management techniques, such as the use of numbing creams or ice.
Understanding the Healing Process
Educating yourself about the healing process is crucial to ensure proper care and minimize potential risks. Different types of ear piercings have varying healing times, ranging from a few weeks to several months. Understanding the signs of healing and potential complications can help you identify any issues and seek appropriate medical attention if necessary.
Taking Care of Personal Hygiene
Maintaining good personal hygiene is important both before and after getting your ear pierced. Cleanse your ears and the surrounding area thoroughly with mild soap and warm water before the procedure. Avoid using harsh chemicals or alcohol-based products as they can irritate the skin. Additionally, keep your hair clean and away from the newly pierced area to prevent infection.
Avoiding Blood Thinners
Certain medications and substances can thin the blood and increase the risk of bleeding during the piercing process. If you are on any blood-thinning medications or regularly consume alcohol, consult with your healthcare provider or piercer to assess if it is safe to proceed with the piercing. It’s important to prioritize your safety and minimize the risk of excessive bleeding or complications.
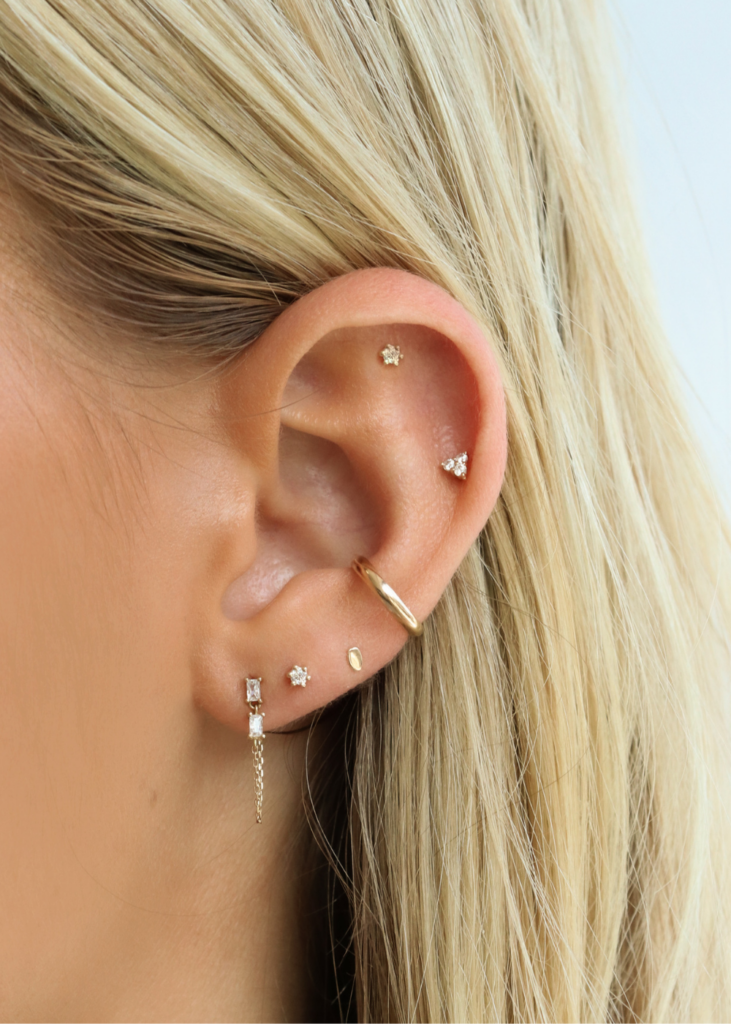
This image is property of bedthreads.com.au.
The Ear Piercing Process
Cleaning the Ear and Marking the Spot
Before the actual piercing takes place, the piercer will clean your ear with an antiseptic solution to ensure a sterile environment. They will then mark the spot where the piercing will be placed. Take your time to review and discuss the placement with the piercer, as this is your opportunity to ensure you are satisfied with the location.
Numbing the Area (Optional)
In some cases, numbing creams or sprays may be used to mitigate discomfort during the piercing process. If you have concerns about pain, discuss this with your piercer beforehand to determine if using a numbing agent is suitable for your specific situation.
Using a Piercing Needle or Gun
Depending on the piercing studio and your chosen piercing, either a piercing needle or gun will be used. Piercing needles are typically used for more complex and cartilage piercings, as they offer more precision and reduce the risk of tissue damage. Piercing guns are commonly used for standard lobe piercings and are known for their speed. Regardless of the instrument used, ensure that it is sterile, properly handled, and disposed of after use.
Inserting the Jewelry
Once the piercing is complete, the piercer will carefully and gently insert the chosen jewelry into the newly pierced hole. They will check the fit and ensure that the jewelry is secure. You may feel some discomfort during this step, but it should be brief and manageable. If you experience excessive pain or discomfort, inform your piercer immediately.
Aftercare Instructions
After the piercing is complete, the piercer will provide you with detailed aftercare instructions. These instructions will include guidance on cleaning, avoiding certain activities, and general care for your new piercing. It is crucial to follow these instructions diligently to promote proper healing and reduce the risk of complications.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Infection and Pus Formation
Infections are one of the most common risks associated with ear piercing. Symptoms of infection include redness, swelling, pain, and the formation of pus. To prevent infections, it is essential to follow proper aftercare instructions, keep the area clean, and avoid touching the piercing with dirty hands. If you suspect an infection, seek medical attention promptly.
Allergic Reactions
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to certain materials used in jewelry, such as nickel. Symptoms may include redness, itching, and inflammation around the pierced area. To minimize the risk of allergic reactions, opt for hypoallergenic jewelry made of materials like surgical stainless steel, titanium, or 14k gold.
Migration or Rejection of Jewelry
In certain cases, the body may reject the jewelry, causing it to move or migrate out of the piercing. Signs of migration or rejection include consistent pain, excessive redness, and movement of the jewelry away from the original placement. If you notice any signs of migration or rejection, consult with a professional piercer or healthcare provider.
Keloids or Hypertrophic Scarring
Keloids and hypertrophic scarring are excessive forms of scar tissue that can develop around a piercing. Keloids are raised, thickened areas of skin that extend beyond the original wound, while hypertrophic scars are raised, red scars confined to the site of the piercing. Individuals with a predisposition to keloid or hypertrophic scarring should carefully consider the risks before getting an ear piercing.
Nerve Damage or Chondritis
While rare, nerve damage and chondritis (inflammation of the cartilage) are potential risks associated with certain ear piercings. It is essential to choose a skilled and qualified piercer who can minimize the risk of these complications. If you experience severe pain, numbness, or unusual symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
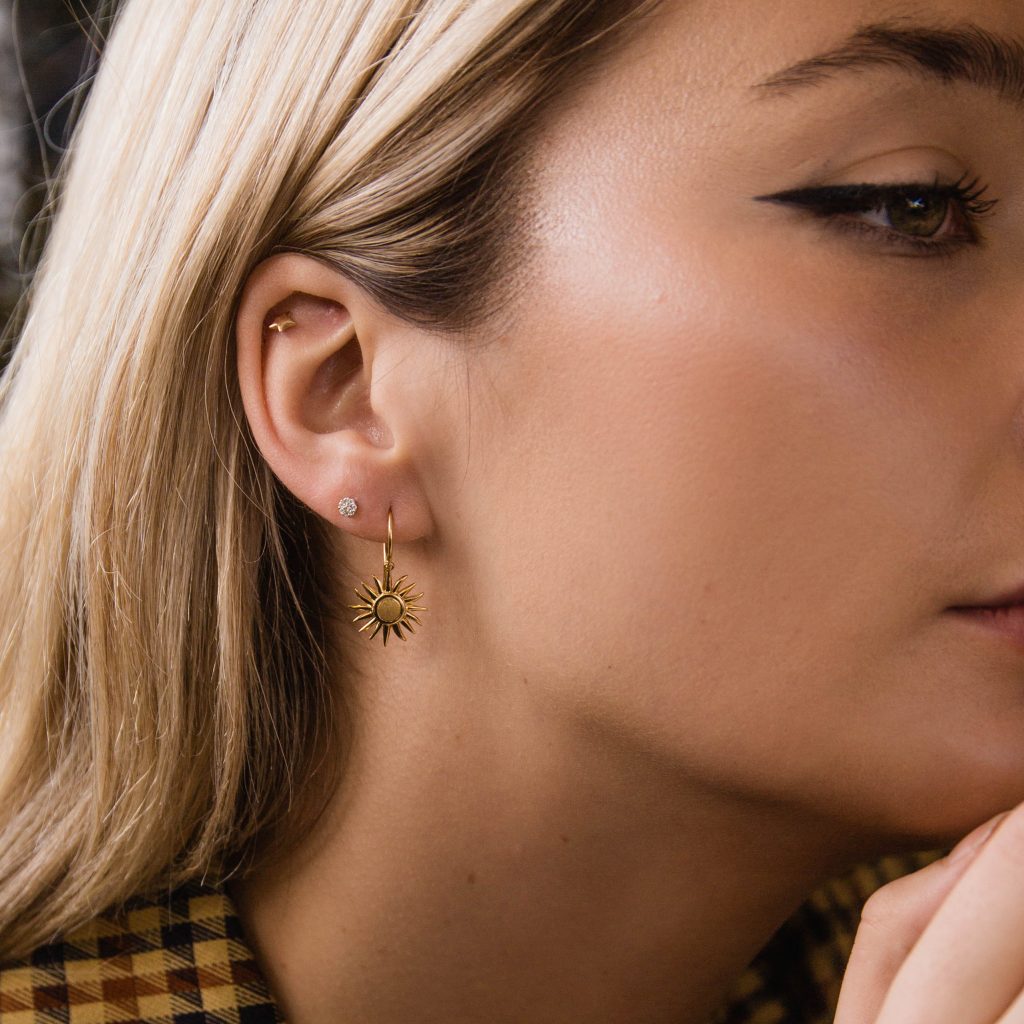

This image is property of www.dinnyhall.com.
Aftercare for Ear Piercing
Cleaning the Piercing
Proper cleaning is crucial for the healing process of your new ear piercing. Cleanse the piercing twice a day with a saline solution or mild saline-based soap, following the aftercare instructions provided by your piercer. Gently rotate the jewelry during cleaning to prevent it from sticking to the skin and forming a crust.
Avoiding Touching or Rotating Jewelry
While it may be tempting to touch or rotate the jewelry, avoid doing so as much as possible, especially with dirty hands. Touching the piercing increases the risk of introducing bacteria, causing irritation or infection. Only touch the piercing when necessary, such as during the cleaning process.
Managing Pain and Swelling
It is normal for some pain and swelling to occur after getting an ear piercing. To manage pain, over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be taken as directed by your healthcare provider. Applying a cold pack or ice wrapped in a clean cloth to the pierced area can also help reduce swelling.
Protecting the Piercing from Irritants
During the healing process, it’s important to protect your piercing from irritants such as hair products, harsh chemicals, and excessive moisture. Avoid swimming in pools, hot tubs, or natural bodies of water until the piercing has fully healed. Additionally, be cautious when using hairspray, shampoo, or other products near the pierced area.
Maintaining Proper Hygiene
Maintaining good overall hygiene is essential for the proper healing of your ear piercing. Keep your hair and bedding clean, as they can harbor bacteria that may impact the healing process. Avoid sleeping on the side of the newly pierced ear to prevent snagging or irritation.
Following Piercer’s Instructions
Your piercer will provide detailed aftercare instructions specifically tailored to your piercing. It is essential to follow these instructions diligently and seek clarification if you have any doubts or concerns. Your piercer is your best resource for guidance and support during the healing process.
Choosing the Right Jewelry
Material Options for Ear Piercing Jewelry
The material of the jewelry you choose for your ear piercings plays a vital role in both comfort and safety. Opt for high-quality materials such as surgical stainless steel, titanium, or 14k gold, as they are less likely to cause allergic reactions. Avoid jewelry made from materials like nickel, which is a common allergen and can lead to irritation or infections.
Styles and Designs
When it comes to ear piercing jewelry, the options are virtually limitless. Consider your personal style, the specific piercing, and the occasion when selecting the jewelry. From elegant studs to statement hoops and dainty dangling earrings, there is a wide variety of styles and designs to cater to individual preferences and enhance your overall look.
Sizing and Gauge
Accurate sizing and gauge selection are crucial for a comfortable and well-fitting piece of jewelry. Consult with your piercer on the appropriate sizing for your specific piercing, as different types of ear piercings require different lengths and gauges. It is essential that the jewelry fits properly to prevent discomfort, irritation, or other complications.
Considering Lifestyle and Activity Level
When choosing jewelry for your ear piercings, consider your lifestyle and activity level. If you lead an active lifestyle or participate in sports, opt for jewelry that is secure, lightweight, and won’t easily get caught or pulled. Additionally, consider whether your work or hobbies require you to remove jewelry for safety reasons, and select jewelry that can be easily taken on and off when necessary.
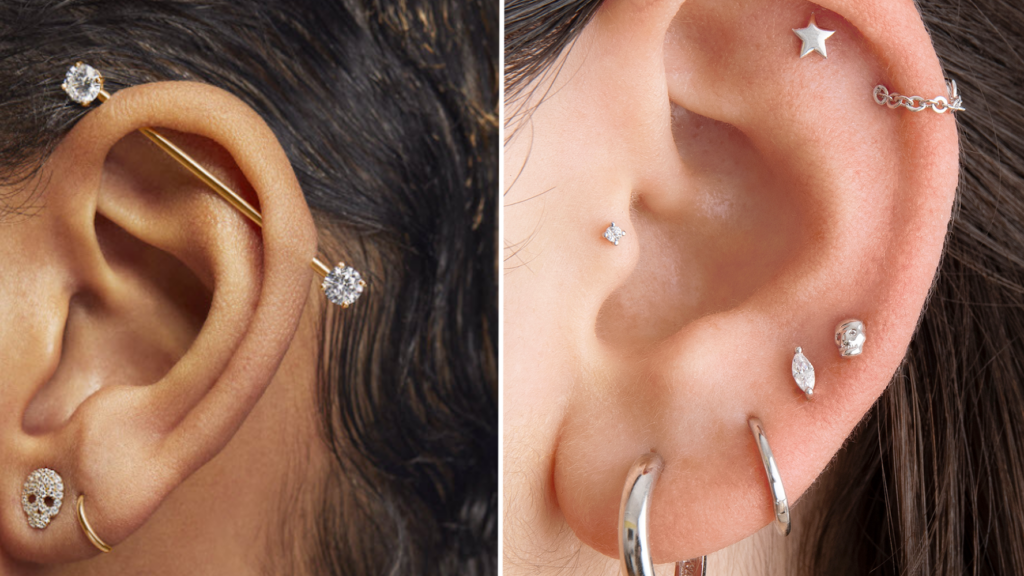
This image is property of media.allure.com.
Ear Stretching and Gauged Earrings
Historical Significance of Ear Stretching
Ear stretching, also known as gauging, is a practice with ancient cultural and historical significance. Various cultures, including indigenous tribes from Africa, Asia, and the Americas, adopted ear stretching as a traditional custom. In these cultures, ear stretching was often a symbol of social status, tribal affiliation, or achieved milestones.
Techniques for Ear Stretching
Ear stretching involves gradually enlarging the pierced hole to accommodate larger gauge jewelry. The process should be approached with caution and patience to ensure proper healing and minimize the risk of complications. Common techniques for ear stretching include using tapers, gradually inserting larger jewelry, or consulting with a professional piercer for assistance.
Choosing the Right Ear Stretching Jewelry
Choosing the right jewelry for stretched ears is crucial for both comfort and aesthetics. Look for jewelry that is specifically designed for stretched lobes, such as plugs or tunnels. Consider the material, size, and shape of the jewelry based on your personal style and preferences. It is essential to give your stretched ears adequate time to heal before changing or swapping jewelry.
Taking Care of Stretched Ears
Proper aftercare is key to the healthy healing of stretched ears. Cleanse the stretched piercings with saline solution, avoiding harsh chemicals or alcohol-based products. As the stretched hole heals, be mindful of potential issues such as tearing, thinning, or blowouts, which can occur if the stretching process is rushed or ill-advised. Seek guidance from a professional piercer if you have any concerns or questions.
Ear Piercing Myths and Facts
Piercing Guns vs. Needles
A common misconception is that piercing guns are safer and more efficient than needles. However, professional piercers generally recommend the use of needles for ear piercings, especially for cartilage piercings. Needles allow for a cleaner and more precise piercing, minimizing the risk of tissue damage and complications.
Pain Level of Ear Piercing
The pain experienced during an ear piercing is subjective and can vary from person to person. Many individuals describe the sensation as a quick pinch or pressure that subsides soon after the piercing is done. Rest assured that ear piercings are generally considered to be relatively low in pain compared to other body piercings.
Ear Piercing and Migraines
A popular belief is that piercing certain areas of the ear, such as the daith piercing, can help alleviate migraines. While some individuals have claimed success in migraine relief with these piercings, scientific evidence supporting this claim is limited. If you suffer from migraines, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before relying solely on ear piercings as a solution.
Ear Piercing and Acupuncture Points
There is a misconception that certain ear piercings, such as the tragus or daith piercing, target specific acupuncture points, leading to various health benefits. While acupuncture does involve specific point stimulation, the placement of ear piercings is not directly aligned with these points. It’s important to approach ear piercings primarily as a form of self-expression and style rather than relying on them for health benefits.
Overall, ear piercing is an ancient practice that has evolved over time to become a popular form of self-expression and individual style. With proper research, preparation, and aftercare, ear piercing can be a safe and enjoyable experience. Remember to consult with a professional piercer, carefully consider the type of piercing and jewelry, and follow the recommended aftercare instructions to ensure the best possible outcome for your new ear piercing.
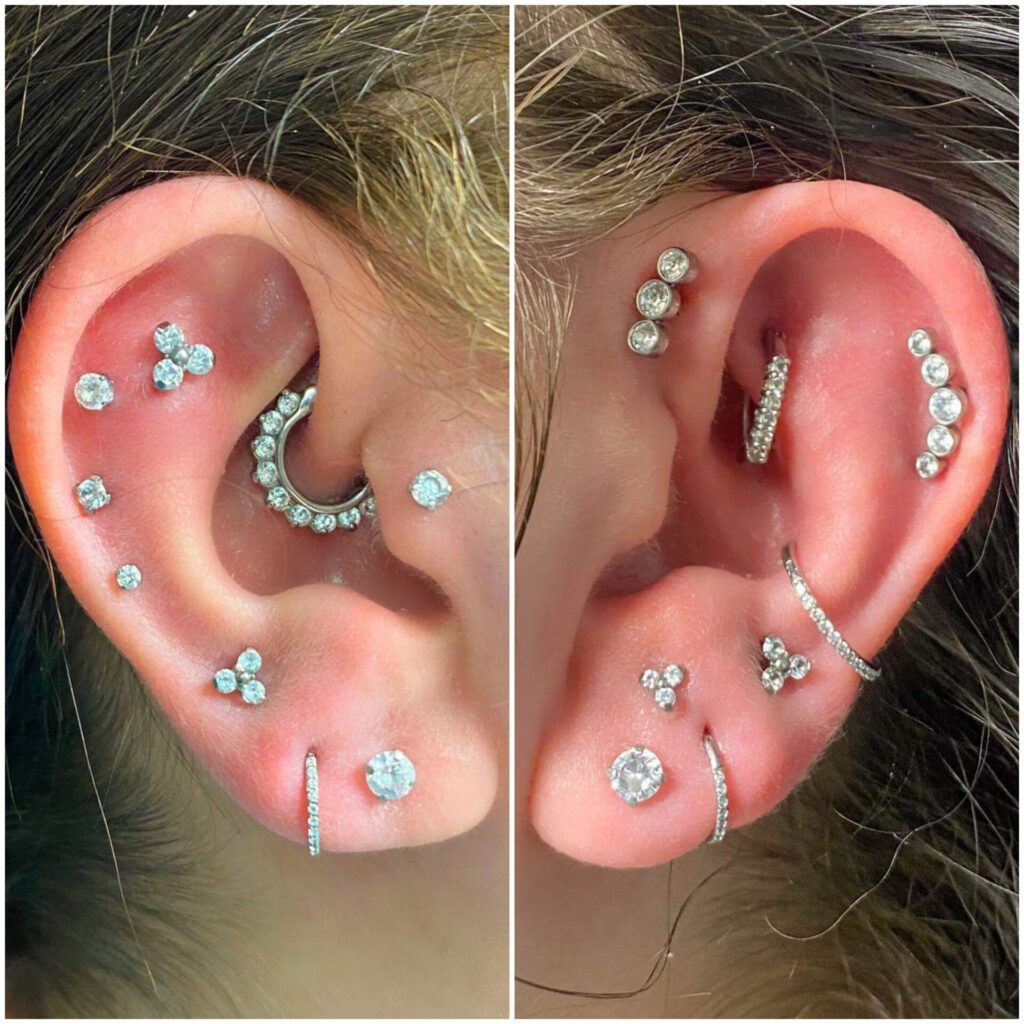
This image is property of i.redd.it.

